Differences between RVVP and KVVRP Cables
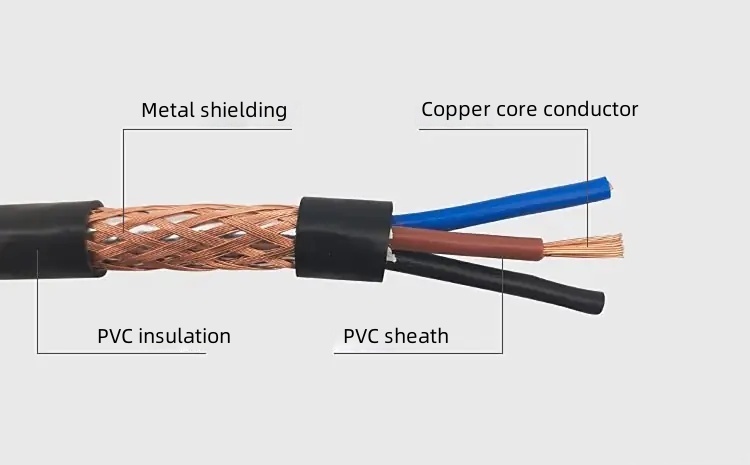
The main differences between RVVP and KVVRP cables lie in their designations, voltage ratings, conductor construction, implementation standards, and application scenarios. RVVP is suitable for 300/300V low-voltage interference-resistant lines, while KVVRP is suitable for 450/750V shielded control applications.
Key Differences Comparison
Name and Definition
RVVP: Copper-core PVC insulated, PVC sheathed, copper braided shielded flexible cable. This is an electrical connection cable with interference-resistant features.
KVVRP: Copper-core PVC insulated, PVC sheathed, braided shielded, flame-retardant Class C control flexible cable. It is designed for areas with high signal interference.
Voltage Ratings
RVVP is rated for 300/300V or 300/500V and is suitable for low-voltage environments.
KVVRP is rated for 450/750V and is suitable for higher-voltage control circuits.
Conductor Structure
RVVP uses a multi-stranded copper wire conductor with excellent flexibility, making it suitable for mobile installations.
KVVRP uses a single rigid copper wire or multi-stranded BV rigid wire, offering a more robust structure and suitable for fixed installations.
Applicable Standards
RVVP complies with JB/T8734.5-2012.
KVVRP complies with GB/T9330-2008.
Application Scenarios
RVVP: Mobile or close-spaced applications requiring interference resistance, such as communications, audio broadcasting, and security monitoring.
KVVRP: Fixed applications with high electromagnetic interference, such as indoor signal control and monitoring circuits.
Other Differences
Shielding Performance: Both include a braided copper shield, but KVVRP emphasizes flame retardancy (Class C).
Bending Radius: Due to its greater flexibility, RVVP has a minimum bending radius of 15 times the outer diameter, while KVVRP typically requires a minimum of 12 times the outer diameter.
TAG:
Previous
Next
Previous:
Next:









